Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that leads to hair loss in small, round patches. If you're one of the many individuals suffering from this condition, you might be wondering: Which medication helps alopecia areata? In this article, we’ll explore the most effective treatments, including FDA-approved medications, natural remedies, and expert-backed solutions. By the end, …
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that leads to hair loss in small, round patches. If you’re one of the many individuals suffering from this condition, you might be wondering: Which medication helps alopecia areata?
In this article, we’ll explore the most effective treatments, including FDA-approved medications, natural remedies, and expert-backed solutions. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the options available to manage alopecia areata and restore your hair health.

What Is Alopecia Areata?
Overview of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair to fall out in small, round patches. It typically starts with small, coin-sized areas of hair loss on the scalp, but can also affect other areas like the eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
The exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Stress, illness, or hormonal changes can trigger or worsen the condition.
Types of Alopecia Areata
There are several variations of alopecia areata, including:
- Alopecia Areata (Patchy): Hair loss occurs in small patches on the scalp or body.
- Alopecia Totalis: Complete loss of all hair on the scalp.
- Alopecia Universalis: Total loss of hair on the scalp and body, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
While alopecia areata is typically not life-threatening, it can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being and quality of life.
Common Medications for Treating Alopecia Areata
Corticosteroids for Alopecia Areata
One of the most commonly prescribed treatments for alopecia areata is corticosteroids. These medications are used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system’s attack on hair follicles.
- Topical Steroids: These are applied directly to the affected areas of the scalp. Topical corticosteroids are generally the first-line treatment for mild cases of alopecia areata.
- Steroid Injections: For more severe cases, corticosteroids can be injected directly into the bald patches. This method is more effective and provides faster results in stimulating hair regrowth.
- Oral Steroids: In cases where topical or injectable steroids are not effective, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for short-term use. However, long-term use of oral steroids is generally not recommended due to potential side effects, such as weight gain, high blood pressure, and osteoporosis.
Effectiveness: Corticosteroids are effective in many cases, but hair regrowth may take several weeks or months. Results can vary from person to person.
Minoxidil (Rogaine) for Hair Regrowth
Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical treatment that promotes hair regrowth. While it’s primarily used to treat androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), it has also been shown to help with alopecia areata.
- How It Works: Minoxidil stimulates hair follicles and encourages hair growth, even in areas where hair loss has occurred.
- Application: Minoxidil is applied directly to the scalp and is typically used twice a day.
- Effectiveness: Minoxidil is more effective for some individuals than others, with results appearing within 6 to 12 weeks of consistent use.
Minoxidil can be combined with other treatments, such as corticosteroid injections, for enhanced results.
Janus Kinase Inhibitors (JAK Inhibitors)
JAK inhibitors are a newer class of medications that have shown promise in treating alopecia areata by targeting immune system signals that cause hair follicles to shrink.
- Examples: Tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and Ruxolitinib (Jakafi) are JAK inhibitors that have been approved for other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis but are now being explored for alopecia areata.
- How They Work: JAK inhibitors block the inflammatory pathways that are responsible for the immune system’s attack on hair follicles.
- FDA Approval: In recent clinical trials, JAK inhibitors have shown significant efficacy in promoting hair regrowth for individuals with alopecia areata, leading to their approval for use in some cases.
Effectiveness: Early results from clinical trials are promising, with many patients experiencing full regrowth within 3 to 6 months of starting treatment.
Topical Immunotherapy
Topical immunotherapy is another treatment option used for severe or extensive cases of alopecia areata. It involves applying a chemical solution, such as diphencyprone (DPCP), to the scalp, which induces an allergic reaction.
- How It Works: The allergic reaction stimulates the immune system and may redirect the body’s immune response, promoting hair regrowth.
- Effectiveness: This method is effective for many individuals with alopecia areata, though the treatment can take several months before noticeable results appear.
Topical immunotherapy is considered one of the most effective treatments for severe cases but may cause side effects like scalp irritation or contact dermatitis.
Natural and Over-the-Counter Treatments
Biotin and Other Supplements
While supplements cannot cure alopecia areata, they can support hair health and help reduce hair thinning. Biotin (Vitamin B7), zinc, and iron are commonly recommended supplements for hair growth.
- Biotin: Known for promoting healthy hair growth, biotin is often used to prevent hair thinning.
- Zinc and Iron: Deficiencies in these minerals can contribute to hair loss, so supplementation may be beneficial in maintaining healthy hair.
Essential Oils for Alopecia Areata
Certain essential oils, such as rosemary oil and lavender oil, are believed to promote hair growth and reduce inflammation. While more research is needed, some studies suggest that these oils can be effective when used as part of a holistic treatment plan for alopecia areata.
- How to Use: Essential oils should be diluted with a carrier oil (e.g., coconut oil) before being massaged into the scalp.
- Effectiveness: These oils can support overall hair health, but they are not a substitute for medical treatments.
Expert Opinions on Alopecia Areata Medications
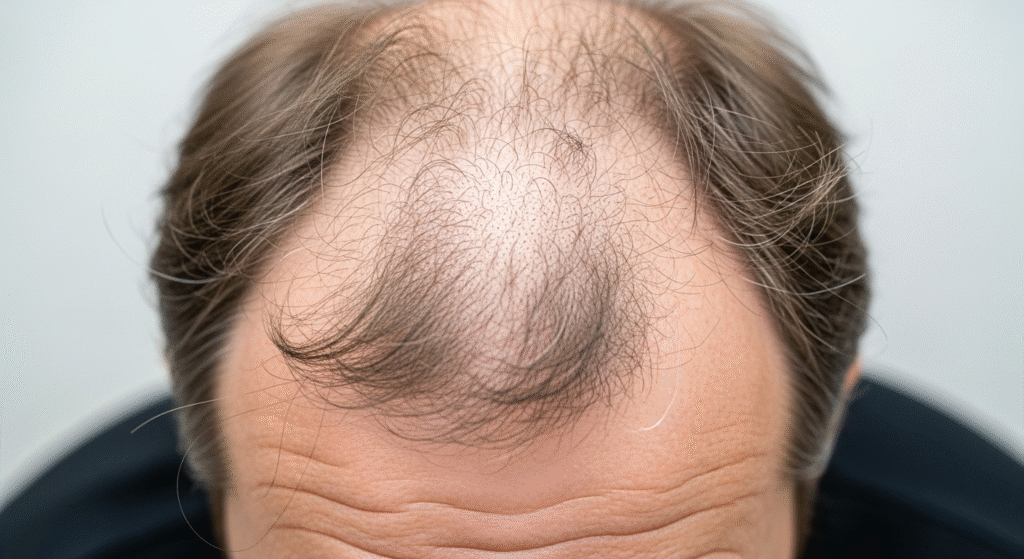
How Effective Are Medications for Alopecia Areata?
The effectiveness of medications for alopecia areata can vary depending on the severity of the condition and how early the treatment is started. Corticosteroids and minoxidil are effective for many people, but results may take several weeks to months. Newer treatments like JAK inhibitors show great promise, but they are still undergoing further research and clinical trials.
Side Effects and Considerations of Alopecia Areata Medications
Potential Side Effects of Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, while effective, can come with side effects, particularly with long-term use:
- Weight gain
- High blood pressure
- Weakened bones
These side effects make corticosteroids a temporary solution, and they should be used under careful medical supervision.
Minoxidil and Its Side Effects
Common side effects of minoxidil include:
- Scalp irritation
- Unwanted facial hair growth
- Rapid heart rate (rare)
Most side effects are mild and temporary, but if they persist, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Side Effects of JAK Inhibitors
JAK inhibitors are still relatively new for alopecia areata, and their long-term side effects are not yet fully understood. Potential risks include:
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Liver enzyme changes
- Headaches and nausea
Patients using JAK inhibitors should be closely monitored by a healthcare provider.
Can Alopecia Areata Be Cured with Medications?
What’s the Prognosis for Alopecia Areata?
While alopecia areata can be managed with medication, there is currently no permanent cure. Most treatments aim to reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth, but hair loss can recur. Early treatment significantly improves the chances of regrowing hair, but it’s essential to manage expectations and understand that relapses may occur.
Long-Term Management of Alopecia Areata
For long-term management, it’s crucial to stay on top of medication and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can help optimize the treatment and minimize relapses.
FAQs
How soon will I see results from alopecia areata medications?
Results can take anywhere from 3 to 6 months after starting treatment, depending on the medication used and the severity of the condition.
Are there any risks with using corticosteroids for alopecia areata?
Long-term use of corticosteroids can cause side effects like weight gain and high blood pressure. They should be used cautiously and under a doctor’s supervision.
Can alopecia areata return after successful treatment?
Yes, alopecia areata can return even after successful treatment. Ongoing management is necessary to prevent relapses.
Is there a permanent cure for alopecia areata?
Currently, there is no permanent cure for alopecia areata, but various treatments can help regrow hair and manage the condition effectively.
Ready To Take Your Next Step
If you’re dealing with alopecia areata, it’s time to take action. Whether you opt for corticosteroids, minoxidil, or JAK inhibitors, the right treatment can help you regain your hair and confidence. Book a consultation with Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon in Islamabad today to discuss your options and start your journey to hair regrowth.