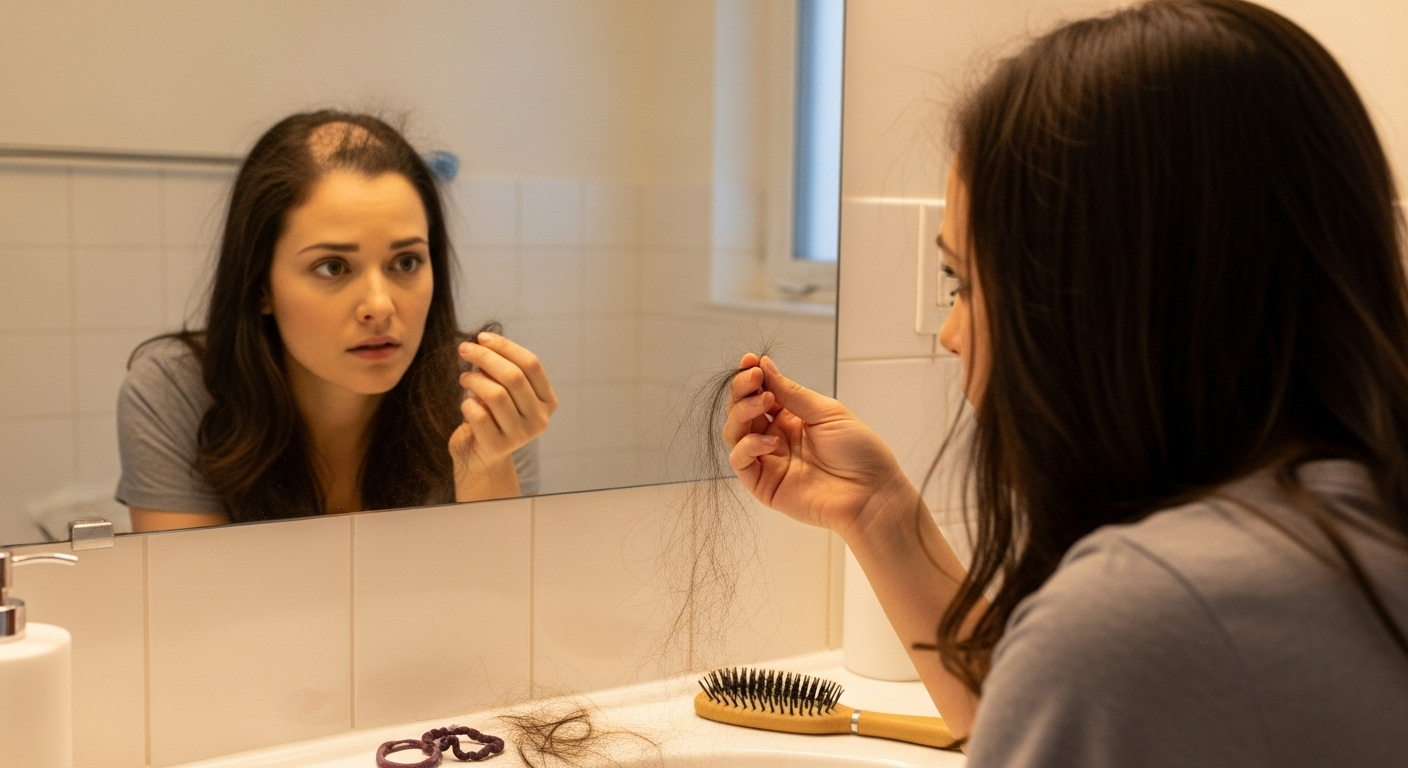
Have you ever wondered what hair really is and how it grows? Understanding the science behind your hair can help you take better care of it and address common hair issues. Whether you're dealing with hair loss, seeking healthy hair growth, or just curious about hair structure, this post will break down everything you need …
Have you ever wondered what hair really is and how it grows? Understanding the science behind your hair can help you take better care of it and address common hair issues. Whether you’re dealing with hair loss, seeking healthy hair growth, or just curious about hair structure, this post will break down everything you need to know. We’ll explore what hair is, how it grows, and the best ways to maintain your hair health.
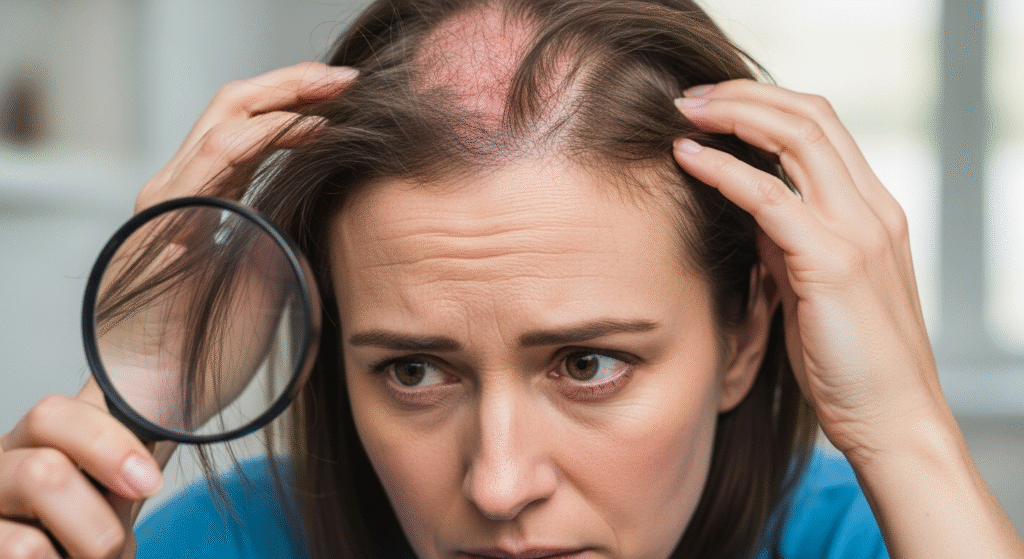

What is Hair?
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles located in the skin. It plays a significant role in protection, aesthetics, and regulating body temperature.
Hair is composed primarily of keratin, a fibrous protein that is produced in hair follicles. While we often focus on the external appearance of hair, its internal structure and function are crucial for understanding its role in overall health.
The Basic Definition of Hair
Hair is a strand of keratinized cells produced in hair follicles. It emerges from the skin’s surface, providing protection, regulating body temperature, and enhancing human appearance.
The Different Types of Hair
There are three primary types of hair:
- Terminal Hair: Thick, long hair found on the scalp, face, underarms, and pubic areas.
- Vellus Hair: Fine, short, and thin hair found on most of the body, particularly on the face and arms.
- Lanugo Hair: Soft, fine hair that covers the fetus in the womb.
The Structure of Hair
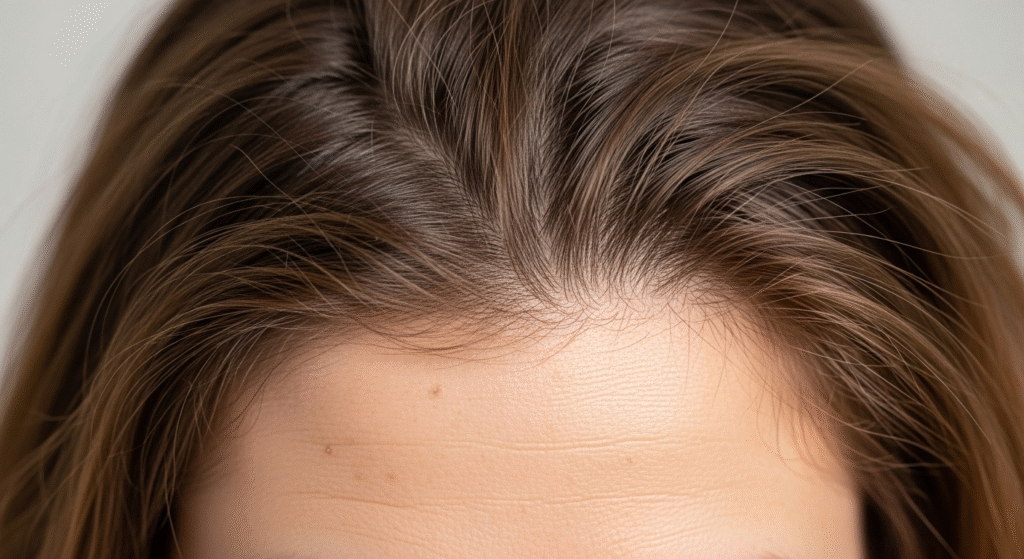

Understanding the structure of hair is essential to managing its health. Hair isn’t just a single strand; it’s a complex structure with multiple components that work together to support growth and function.
The Hair Shaft
The hair shaft is the visible part of the hair that extends beyond the scalp. It consists of three layers:
- Cuticle: The outermost layer, made up of overlapping scales that protect the hair.
- Cortex: The middle layer that contains melanin, responsible for the hair’s color and strength.
- Medulla: The innermost layer, found in thicker hairs, providing structure.
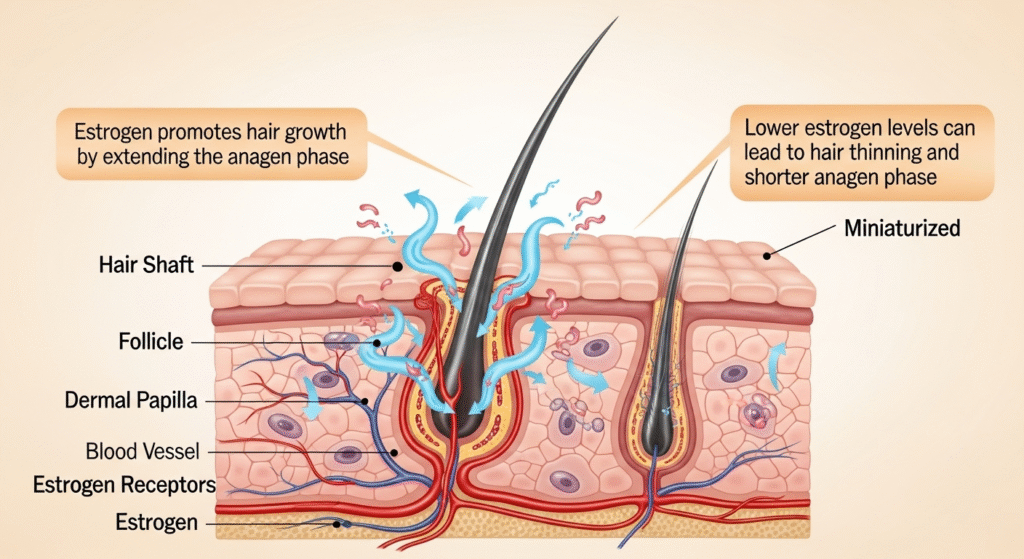
The Hair Follicle
The follicle is where hair growth begins. It’s a tiny organ in the skin that houses the root of the hair. The follicle includes several components:
- Hair Bulb: The base of the follicle where hair cells are produced.
- Hair Papilla: Contains blood vessels that nourish hair growth.
- Matrix: Cells in the matrix divide and push upward to form the hair shaft.
Sebaceous Glands and Hair Growth
Each hair follicle is connected to a sebaceous gland, which produces sebum. Sebum is a natural oil that keeps the hair and scalp moisturized, preventing dryness and brittleness.
The Hair Growth Cycle
Hair grows in a cycle that can last for several years. This cycle is divided into three stages: the Anagen phase, the Catagen phase, and the Telogen phase. Understanding this cycle is key to understanding how hair grows, falls out, and regrows.
The Anagen Phase (Growth Phase)
The Anagen phase is the active growth phase of the hair. Hair in this phase grows at an average rate of half an inch per month and can last for 2–7 years. The longer the Anagen phase, the longer the hair can grow.
The Catagen Phase (Transitional Phase)
The Catagen phase is a short transitional phase that lasts about 2–3 weeks. During this phase, hair growth stops, and the hair follicle shrinks.
The Telogen Phase (Resting Phase)
The Telogen phase is a resting phase that lasts about 3–4 months. Hair does not grow during this phase, and old hairs are eventually shed as new hair begins to grow in its place.
Why is Hair Important?
Hair plays many roles beyond aesthetics. It’s more than just something that grows on your head—it’s a multifunctional feature with health benefits.
Hair’s Role in Protection
Hair helps protect the scalp from the sun’s harmful UV rays. It also provides a barrier against dirt, dust, and other particles that could harm the scalp.
Hair’s Role in Sensory Functions
Hair follicles are sensitive to touch, helping to detect environmental changes. This sensitivity helps us respond to stimuli such as wind or movement, particularly facial and body hair.
Cultural and Social Significance of Hair
Throughout history, hair has held cultural significance. In many societies, hair length, style, and color are linked to identity, status, and personal expression.
Factors Affecting Hair Growth and Health
Hair health isn’t just about genetics; various external and internal factors can influence growth, thickness, and quality.
Genetics and Hair Type
Genetics determine your natural hair texture, color, and growth pattern. For instance, curly hair grows at a slower rate than straight hair.
Hormonal Changes and Their Impact on Hair
Hormonal fluctuations caused by puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can lead to hair thinning or loss. Conditions like thyroid imbalances can also significantly affect hair health.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to sun, pollution, and harsh weather conditions can lead to dry, damaged hair. Pollution, in particular, can cause hair follicles to become clogged, inhibiting healthy growth.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet plays an essential role in hair health. Nutrients like biotin, vitamin E, and iron are necessary for optimal hair growth. Poor nutrition can result in hair thinning and loss.
Hair Care Tips for Healthy Hair
Maintaining healthy hair involves proper care and the right routine. Here are some tips to keep your hair healthy and strong:
Proper Shampooing and Conditioning Techniques
Use mild shampoos suited to your hair type. Shampoo hair 2–3 times a week to avoid stripping it of natural oils. Condition hair to provide moisture and prevent dryness.
Protecting Hair from Damage
Avoid excessive heat styling and chemical treatments. Always use heat protectants before blow-drying or flat-ironing to prevent damage.
Regular Scalp Care
Maintaining a healthy scalp is essential for hair growth. Use scalp treatments like oils and serums to stimulate the follicles and prevent buildup that can block hair growth.
Common Hair Problems and Solutions
Hair can experience a variety of issues, from hair loss to damage, but many of these problems are treatable.
Hair Loss and Thinning
Common causes of hair loss include genetics, stress, poor diet, and medical conditions. Treatments such as Minoxidil, Finasteride, and hair transplants are effective in combating hair loss.
Dandruff and Scalp Conditions
Dandruff is often caused by a dry scalp or fungal infections. Use anti-dandruff shampoos or consult a dermatologist for stronger treatments if necessary.
Dry, Damaged Hair
Dry hair can be caused by environmental factors, over-styling, or using harsh hair care products. Use moisturizing shampoos, conditioners, and deep conditioning treatments to restore moisture.
Hair Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths surrounding hair care. Let’s debunk a few common ones.
Shaving Hair Makes It Grow Back Thicker
Shaving hair does not affect its thickness or growth rate. It only gives the appearance of thicker hair due to the blunt ends left by shaving.
You Can’t Grow New Hair After a Certain Age
While hair growth does slow down with age, it is still possible to grow new hair with the right treatments. Early intervention can make a significant difference.
Brushing Your Hair 100 Times a Day Promotes Growth
Excessive brushing can actually damage hair and cause breakage. It’s essential to brush hair gently and avoid over-styling.
FAQs
What Causes Hair Loss?
Hair loss can be caused by genetics, stress, hormonal changes, and poor diet. Medical conditions like alopecia and thyroid imbalances can also contribute.
How Often Should I Wash My Hair?
It depends on your hair type. People with oily hair may need to wash it daily, while those with dry hair may wash it 2-3 times a week.
Can Diet Improve Hair Growth?
Yes, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals like biotin, iron, and vitamin D can promote healthier hair growth.
Does Stress Cause Hair Loss?
Yes, prolonged stress can cause hair loss due to telogen effluvium, a condition where hair follicles prematurely enter the shedding phase.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Hair is an essential part of our body that plays several key roles, from protecting our scalp to defining our appearance. Understanding what hair is and how it grows can help you take better care of it and address issues like hair loss.
Book a Consultation with Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon and a Hair Specialist in Islamabad Today
If you’re experiencing hair loss or other hair issues, don’t hesitate to consult with a specialist. They can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your unique needs.