Severe hair fall reasons can feel alarming and confusing, especially when the shedding seems sudden or unexplainable. This article breaks down the major causes of severe hair fall, from hormonal changes and nutritional deficiencies to autoimmune conditions and daily styling damage. By the end, you’ll learn how to identify the triggers, what treatments work best, …
Severe hair fall reasons can feel alarming and confusing, especially when the shedding seems sudden or unexplainable. This article breaks down the major causes of severe hair fall, from hormonal changes and nutritional deficiencies to autoimmune conditions and daily styling damage.
By the end, you’ll learn how to identify the triggers, what treatments work best, and how to start your recovery journey. With expert insights, medical accuracy, and practical solutions, this guide gives you clarity and confidence to regain healthier, stronger hair.
Understanding Severe Hair Fall
What constitutes “severe” hair fall?
While losing 50–100 strands per day is normal, shedding beyond this—especially in clumps, bald patches, or rapid thinning—is classified as severe hair fall. This type of loss often signals an underlying health or lifestyle problem rather than routine shedding.
Key terms explained
- Telogen Effluvium: Sudden shedding after stress, illness, or hormonal change.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Hereditary, patterned hair thinning (common in both men and women).
- Alopecia Areata: Autoimmune condition where the body attacks its own hair follicles.
Common Underlying Causes of Severe Hair Fall
Genetic and Hormonal Factors
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Runs in families and leads to gradual thinning.
- Hormonal Shifts: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and thyroid disorders can trigger heavy shedding.
Pro Tip: If you notice thinning at your hairline or crown and your family history includes baldness, genetics may play a key role.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Hair growth depends on proper nutrition. Common deficiencies include:
- Iron deficiency (anemia)
- Protein shortage (hair is 95% protein-based keratin)
- Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, and Zinc deficiencies
Expert Insight: According to dermatologists, iron deficiency is one of the top correctable causes of hair fall in women under 40.
Immune-Mediated and Medical Conditions
- Alopecia Areata: Immune cells mistakenly attack hair follicles.
- Scalp infections: Fungal infections like ringworm damage the scalp.
- Skin disorders: Psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis weaken follicles.
- Underlying illnesses: Diabetes, lupus, and even untreated syphilis can manifest as hair fall.
Physical and Psychological Stressors
Severe stress or trauma can shock hair follicles into a resting phase:
- Emotional stress, surgery, childbirth, or high fever often trigger telogen effluvium.
- Rapid weight loss or crash dieting is another frequent culprit.
Styling, Traction, and Chemical Damage
- Traction Alopecia: Caused by tight hairstyles, ponytails, or braids.
- Heat and chemical exposure: Frequent straightening, bleaching, or perming weakens hair shafts.
- External damage: Helmets, hair extensions, and over-brushing all contribute.
Other Less Common Yet Important Causes
- Medication Side Effects: Chemotherapy, antidepressants, and beta-blockers can lead to sudden loss.
- Poisoning: Heavy metals like arsenic or lithium exposure.
- Emerging Research: Some studies suggest COVID-19 or vaccination stress response can trigger temporary shedding.
Diagnosing the Cause of Hair Fall
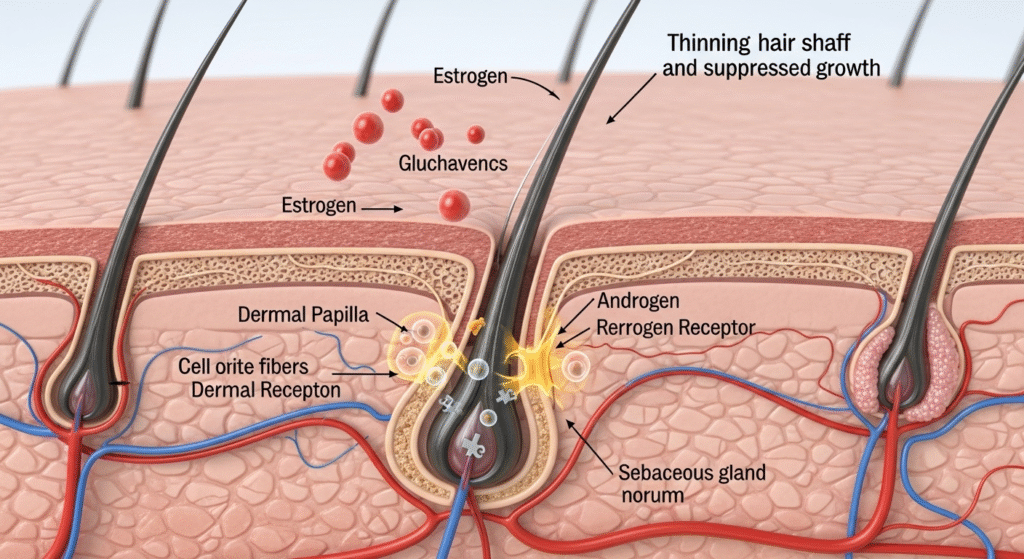
When to Seek Medical Help
If your hair fall is sudden, patchy, or accompanied by scalp irritation, consult a dermatologist promptly.
Diagnostic Tools
- Scalp examination and pull test
- Blood tests to check for anemia, thyroid function, vitamin deficiencies
- Scalp biopsy for suspected autoimmune conditions
Interpreting Results
Matching symptoms (pattern, speed, and scalp health) with test outcomes helps pinpoint the root cause.
Tailored Treatment & Recovery Steps
Medical Treatments
- Nutrient supplementation (iron, vitamin D, protein)
- Hormone correction (thyroid medication, PCOS treatment)
- Corticosteroids for alopecia areata
- Topical Minoxidil or oral Finasteride (under medical supervision)
At-Home Care & Lifestyle Adjustments
- Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos
- Eat a balanced, protein-rich diet
- Practice stress-reduction techniques: yoga, meditation, or therapy
- Avoid harsh hairstyles and chemicals
Advanced Therapies
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy to stimulate regrowth
- Low-level laser therapy for follicle stimulation
- Hair transplantation in advanced genetic cases
FAQs
1. What daily hair loss is normal?
50–100 strands per day is typical. More than that may indicate a problem.
2. Can hair fall be prevented completely?
Not always, but early diagnosis and proper care minimize damage.
3. How long before I see regrowth?
Depending on the cause, regrowth may start within 3–6 months.
4. Is hair fall after COVID-19 permanent?
Most COVID-related hair loss is temporary and reversible.
5. When should I see a dermatologist?
If hair fall is sudden, patchy, or persistent beyond 3 months.
Ready To Take Your Next Step
Are you struggling with unexplained or severe hair fall? Don’t wait until thinning becomes permanent. Book a consultation with Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon in Islamabad today and take the first step toward restoring your confidence and healthy hair.