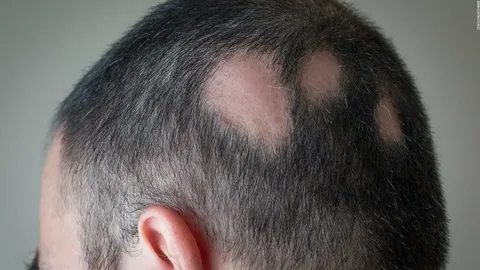
IntroductionAre you noticing sudden patches of hair loss? You might be dealing with alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that leads to hair falling out in small, round patches. In this article, we’ll explore how to diagnose alopecia areata and the most effective topical treatments for managing the condition. With the right knowledge and treatments, you can effectively manage symptoms and work toward regrowing your hair.
Whether you’re seeking a diagnosis or treatment options, this guide will help you navigate the journey with expert insights.

Understanding How to Diagnose Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss, typically in small, round patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair fall. While the exact cause is still unknown, genetics, stress, and environmental factors are believed to play significant roles in its development.
Prevalence: Alopecia areata affects about 2% of the global population, with the majority of cases developing during childhood or adolescence. It’s equally common in both men and women, and it can occur at any age.
Symptoms: The primary symptom of alopecia areata is the sudden onset of bald patches on the scalp or body. Other symptoms include tingling or itching sensations in the affected area and changes in the nails, such as pitting or ridging.
Types of Alopecia Areata
There are different forms of alopecia areata, ranging from localized patches to total loss of hair:
- Patchy alopecia areata: Hair loss in small, round patches.
- Alopecia totalis: Complete loss of hair on the scalp.
- Alopecia universalis: Total hair loss on the scalp and body.
- Ophiasis: A band-like pattern of hair loss around the sides and lower back of the scalp.
Diagnosing Alopecia Areata
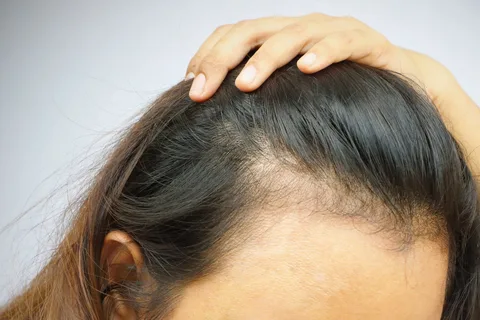
Accurate diagnosis of alopecia areata is essential for effective treatment. Here are the common methods used by healthcare professionals:
Clinical Examination
A dermatologist typically begins by examining the pattern of hair loss. In most cases, alopecia areata causes distinct, round patches of baldness. The doctor may also inspect the nails for signs of pitting or abnormal ridges.
Trichoscopy
This non-invasive procedure involves using a dermatoscope to examine the scalp closely. Trichoscopy allows dermatologists to identify key features of alopecia areata, such as “exclamation mark hairs” (short, broken hairs) and yellow dots, which are indicative of this condition.
Hair Pull Test
To assess the degree of hair shedding, the doctor may perform a hair pull test, where small sections of hair are gently pulled to see how many hairs come out. Excessive shedding in a specific area can indicate alopecia areata.
Scalp Biopsy
In rare cases, if the diagnosis remains unclear, a scalp biopsy may be recommended. This involves taking a small sample of scalp tissue to examine under a microscope. A biopsy helps confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes of hair loss.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can be useful for ruling out other autoimmune diseases or underlying health conditions that could contribute to hair loss.
Topical Treatments for Alopecia Areata

Once diagnosed, there are several topical treatments available to manage alopecia areata. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the affected areas, and the individual’s response to previous treatments.
Topical Corticosteroids
Mechanism: Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory drugs that help reduce immune system activity around hair follicles. When applied topically, they can help reduce inflammation and stimulate hair regrowth in the affected areas.
Effectiveness: Topical corticosteroids are one of the most commonly used treatments for mild cases of alopecia areata. They can be applied directly to the affected patches twice a day for several weeks. While they may not work for everyone, they can provide significant hair regrowth for some individuals.
Application: A dermatologist will usually prescribe corticosteroids in the form of creams, ointments, or lotions. Stronger forms, such as corticosteroid injections, may be used for more severe cases.
Topical Minoxidil
Mechanism: Minoxidil is a topical solution that stimulates hair growth by enlarging hair follicles and prolonging the growth phase of hair.
Effectiveness: While minoxidil is most commonly used for male-pattern baldness, it has shown promise for alopecia areata as well. It is applied directly to the affected scalp areas twice a day. Minoxidil can take 4 to 6 weeks to show visible results, and continuous use is required for sustained hair regrowth.
Side Effects: Some users may experience scalp irritation or unwanted hair growth in surrounding areas, such as the forehead.
Topical Immunotherapy
Mechanism: Topical immunotherapy involves applying chemicals like diphencyprone (DPCP) to the affected area, which induces mild allergic contact dermatitis. This allergic reaction triggers the immune system to “reset” and potentially allow for hair regrowth.
Effectiveness: This treatment is effective for individuals with widespread or recurrent alopecia areata. It may take several months to see results, and repeat treatments are necessary.
Side Effects: Possible side effects include irritation or allergic reactions at the treatment site.
JAK Inhibitors
Mechanism: JAK inhibitors (e.g., ritlecitinib, deucrizotinib) work by blocking specific enzymes that contribute to inflammation in autoimmune diseases, including alopecia areata. These medications are showing promising results in clinical trials.
Effectiveness: JAK inhibitors have been approved for treating severe cases of alopecia areata. They help by targeting the root cause of hair loss, rather than just managing symptoms. However, they are typically prescribed when other treatments have not been effective.
Side Effects: Long-term safety and effectiveness are still under study, and these drugs may have significant side effects, such as immune suppression.
Managing Alopecia Areata
Beyond treatments, managing alopecia areata involves emotional support and lifestyle adjustments.
Emotional Support
The emotional toll of alopecia areata can be significant. It’s important to seek counseling or support groups to help cope with the psychological effects. Sharing experiences with others who understand can be therapeutic and help improve overall well-being.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Stress has been shown to trigger or worsen alopecia areata. Practicing stress-relieving activities such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can be beneficial. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and proper hair care routines can support overall hair health.
Monitoring
Regular follow-ups with your dermatologist are essential for assessing the effectiveness of treatments. Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan or recommend alternative therapies if needed.
FAQs
Can alopecia areata be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for alopecia areata, but treatments can help manage the condition and promote hair regrowth.
Is alopecia areata hereditary?
Genetics play a role in the development of alopecia areata, making it more likely if you have a family member with the condition.
Are there any natural remedies for alopecia areata?
While some individuals turn to essential oils or other natural treatments, there is limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness. It’s always best to consult a dermatologist before trying alternative treatments.
How long does it take to see results from treatment?
Hair regrowth can typically be seen within 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the treatment and individual response.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata is a challenging condition, but with early diagnosis and the right treatment, it is possible to manage and even reverse some of the effects. If you’re experiencing symptoms of alopecia areata, consult with a board-certified dermatologist to discuss your options. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and more effective hair regrowth.
If you’re looking for personalized treatment options or have questions about managing alopecia areata, book a consultation with our experienced dermatologists Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon in Islamabad today. We can guide you through the diagnosis and recommend the best treatment plan tailored to your needs.