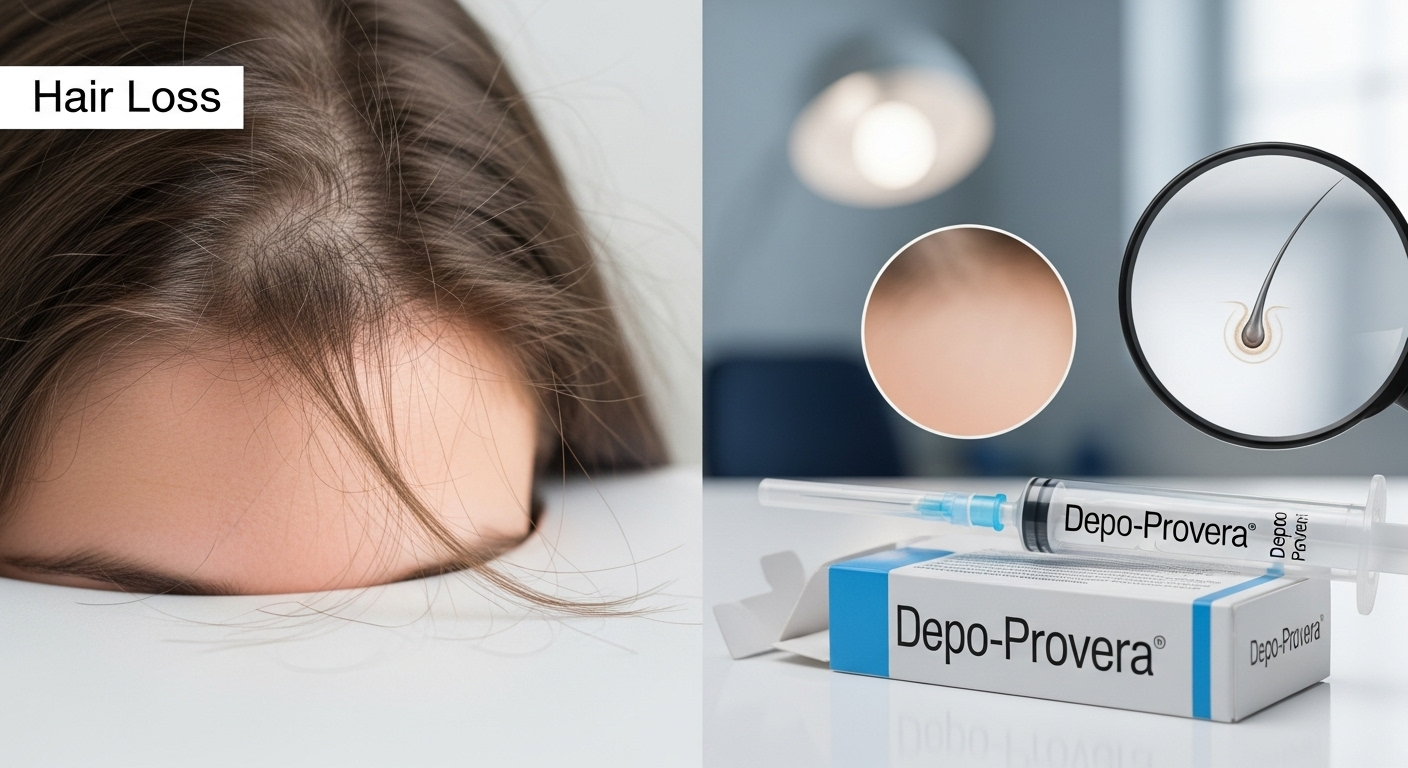
Summary Depo-Provera, a popular contraceptive shot, is sometimes linked to hair loss due to its hormonal effects. This article explains how and why it happens, how common it is, what signs to watch for, and realistic recovery expectations. You’ll also learn practical solutions, expert tips, and safe next steps if you’re experiencing thinning or shedding …
Summary
Depo-Provera, a popular contraceptive shot, is sometimes linked to hair loss due to its hormonal effects. This article explains how and why it happens, how common it is, what signs to watch for, and realistic recovery expectations. You’ll also learn practical solutions, expert tips, and safe next steps if you’re experiencing thinning or shedding while using Depo.
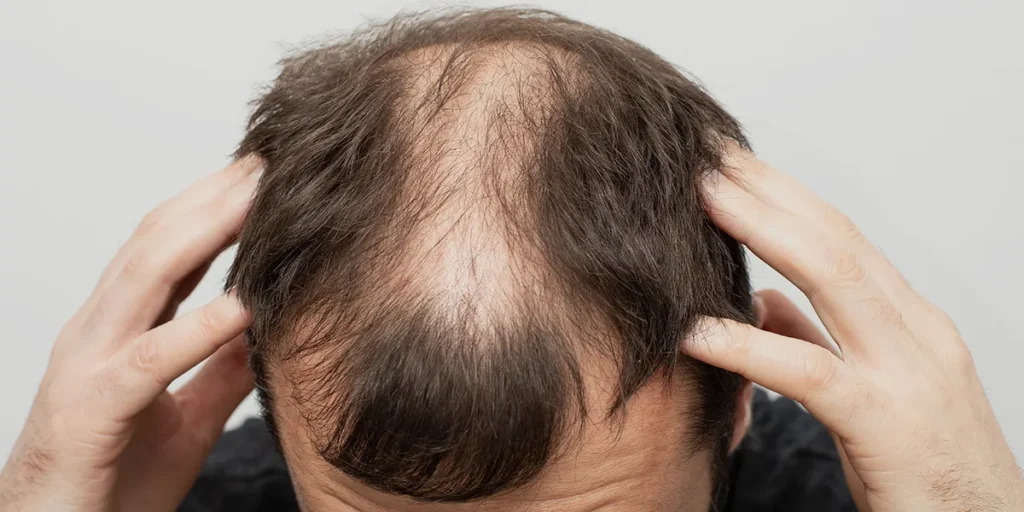
Table of Contents
Introduction
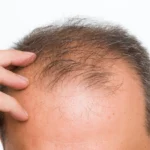
If you’ve noticed unusual shedding after starting birth control, you may be asking: does hair loss and Depo Provera really go hand in hand? Depo-Provera, a progestin-only contraceptive shot, has been reported to cause thinning in some users. In this article, you’ll discover how Depo affects your hair, what recovery looks like, and expert-backed steps to manage the problem with confidence.
Understanding Depo-Provera (DMPA) and Its Mechanism
What is Depo-Provera?
Depo-Provera is an injectable contraceptive containing medroxyprogesterone acetate, a form of synthetic progesterone. It prevents pregnancy by stopping ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and altering the uterine lining.
How the Injection Works
Each shot delivers a slow release of progestin over three months. Unlike combination contraceptives, it contains no estrogen, which plays a protective role in hair growth cycles. This difference explains why some users may notice changes in their hair.
Why Estrogen Matters
Estrogen helps keep hair in the growth (anagen) phase longer. Without it, progestin dominance can sometimes trigger hair follicles to shift into the resting (telogen) phase, leading to shedding.
The Connection: Hair Loss and Depo Provera — What Evidence Says
Clinical Reports and Data
Hair loss is listed as a recognized side effect of Depo-Provera. Studies note that up to 10% of users discontinued use due to this concern. While not extremely common, it’s enough to be clinically relevant.
Mechanisms Behind Hair Loss
- Hormonal shifts: Progestins may act as weak androgens, causing androgenic hair loss in predisposed individuals.
- Telogen effluvium: A sudden change in hormones can push hair prematurely into the shedding phase.
- Follicle sensitivity: Women with a genetic tendency toward female pattern hair loss are more vulnerable.
Risk Factors
- Family history of thinning or baldness
- Existing hormonal imbalances (thyroid disorders, PCOS)
- Nutritional deficiencies (iron, vitamin D, zinc)
How Common Is Hair Loss With Depo?
Incidence and Statistics
Reports suggest that 1 in 40–50 women may experience noticeable hair changes while using Depo. Some describe mild shedding; others report visible thinning at the crown or part.
Underreporting Issues
Because hair loss is gradual and often blamed on stress or diet, true numbers may be higher. Many cases go undocumented in clinical trials.
Shedding vs. Thinning
- Shedding: temporary, diffuse hair loss across the scalp.
- Thinning: gradual reduction in volume, often harder to reverse.
Signs, Symptoms, and When to Be Concerned
Typical Patterns
- General thinning around the crown
- Widening of the part line
- Increased shedding in the shower or on pillows
Onset and Duration
Hair loss typically appears within 3–6 months of starting Depo. Some women notice changes after the first or second injection.
Red Flags
Seek medical help if:
- Shedding is sudden and patchy
- Hair loss is accompanied by fatigue, brittle nails, or unexplained weight change
- Scalp irritation or scarring develops
Recovery Expectations & Timeline
What Happens After Stopping Depo
Once injections are discontinued, hormone levels begin to stabilize. Hair follicles gradually re-enter their natural growth cycle.
General Timeline
- 0–3 months: Shedding may continue as hormones rebalance
- 3–6 months: Shedding slows, early regrowth begins
- 6–12 months: Noticeable volume recovery in most women
- 12–18 months: Hair may return to baseline, though some thinning could remain if genetically predisposed
Incomplete Recovery
For a minority, androgenic effects may cause permanent miniaturization of follicles, especially if there’s a family history of hair loss.
What You Can Do While Still Using Depo or After Stopping

Diagnostic Steps
- Blood work: thyroid panel, ferritin, vitamin D, zinc
- Dermatologist exam: scalp analysis, dermoscopy
Nutrition and Lifestyle
- Prioritize protein and omega-3s
- Manage stress with mindfulness or yoga
- Sleep 7–8 hours to support hormonal balance
Medical Interventions
- Topical minoxidil: stimulates regrowth
- Spironolactone: counters androgenic activity (prescription)
- PRP therapy: platelet-rich plasma injections to boost growth
Hair Care Best Practices
- Use gentle shampoos without sulfates
- Avoid excessive heat or tight hairstyles
- Massage scalp to improve circulation
Alternative Contraceptives
- Lower-androgen progestins
- Combination pills with estrogen
- Non-hormonal options (copper IUD, condoms)
Who Is at Higher Risk / Predictors
- Women with family history of female pattern hair loss
- Those with thyroid or PCOS
- Users with nutrient deficiencies
- Long-term Depo users
Patient Stories & Case Studies
- Case Study 1: 28-year-old woman noticed diffuse shedding 4 months after first Depo shot. Regrowth began 7 months post-discontinuation.
- Case Study 2: Teen user discontinued Depo after one year due to noticeable thinning. Switched to a low-androgen pill with improved outcomes.
Clinical Insights
According to a dermatologist in Islamabad, “Hair loss linked to Depo-Provera is not always permanent. Identifying whether it is due to telogen effluvium or androgenic influence is key. Early intervention greatly improves the chance of full recovery.”
FAQs
Q: Is hair loss from Depo permanent?
A: In most cases, hair regrows within a year of stopping. Permanent loss occurs only in those genetically predisposed.
Q: Can I treat hair loss while still on Depo?
A: Yes. Topical minoxidil and supportive nutrition can help, but results vary.
Q: How soon after stopping Depo will shedding stop?
A: Usually within 3–6 months, but full recovery may take up to 12 months.
Q: What are alternatives if I’m worried about thinning?
A: Low-androgen contraceptives or non-hormonal methods are safer for hair health.
Q: Does taking vitamins help?
A: Only if you’re deficient. Testing is recommended before supplementing.
What’s the Right Next Step:
If you’re experiencing mild shedding, start with nutrition and gentle hair care. If shedding is moderate or severe, consult a dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment. Consider switching contraceptives if hair loss continues.
Book a consultation with Dr. Uzma Irfan in Islamabad today to explore safe options for managing hair loss and finding the best contraceptive plan for your health.