Wondering if your hair loss is genetic? A genetic hair loss test analyzes your DNA to assess your inherited risk of baldness—helping you take early, personalized action. Whether you're seeing early signs of thinning or have a strong family history, this test offers clarity, tailored prevention strategies, and confidence in choosing the right treatments. Backed …
Wondering if your hair loss is genetic? A genetic hair loss test analyzes your DNA to assess your inherited risk of baldness—helping you take early, personalized action. Whether you’re seeing early signs of thinning or have a strong family history, this test offers clarity, tailored prevention strategies, and confidence in choosing the right treatments.
Backed by science and trusted by hair experts, it’s a smart first step in managing your hair health for the long term.
What Is a Genetic Hair Loss Test?
A genetic hair loss test analyzes your DNA to evaluate your likelihood of developing hereditary hair loss, especially androgenetic alopecia (commonly known as male or female pattern baldness). The test does not diagnose current hair loss, but it identifies whether you’re genetically predisposed to it.
The test usually looks for variations in certain genes related to hair growth cycles, hormone sensitivity, and inflammation. By identifying these variants, it helps predict whether you are at increased risk for early-onset or advanced hair thinning.
How Does Genetic Hair Loss Testing Work?
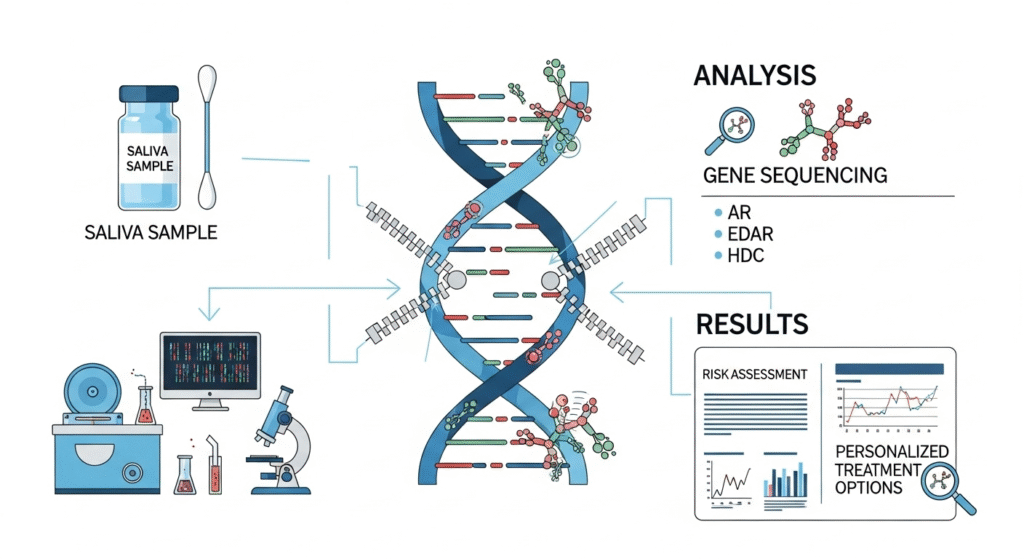
Step-by-Step Process:
- Sample Collection: Most companies send you a testing kit that includes a saliva or cheek swab kit.
- DNA Analysis: Your DNA sample is sent to a lab where it’s analyzed for specific gene variants linked to hair loss.
- Risk Report: After a few weeks (usually 2–6), you receive a report indicating your risk level and potentially treatment suggestions.
Which Genes Are Typically Tested?
Genetic hair loss tests typically focus on:
- AR gene (Androgen Receptor): Strongly associated with androgenetic alopecia.
- Chromosome 20p11 loci: Linked to male-pattern baldness.
- Other hair-related genes: Some tests may include genes influencing inflammation, vitamin metabolism, or scalp health.
These genes help predict how your body processes hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a key contributor to follicle shrinkage and eventual baldness.
What Do the Test Results Show?
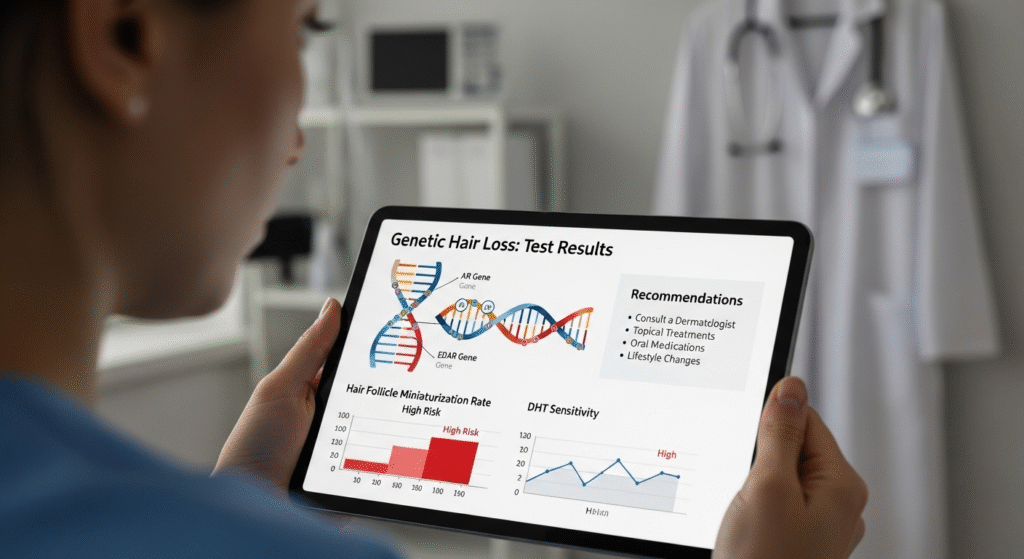
A typical report includes:
- Risk Score: Indicates your genetic likelihood of experiencing pattern baldness.
- Hair Traits: May include predictions about hair thickness, growth cycles, and hair loss onset age.
- Treatment Guidance: Some tests suggest which medications or ingredients may be more effective based on your genetic profile.
While the test cannot give a definitive answer about your hair future, it provides probability-based insights that can guide early preventive steps.
Benefits of Taking a Genetic Hair Loss Test

- Early Detection
Even before hair thinning becomes visible, genetic testing can help you understand your risk, allowing timely prevention. - Personalized Treatment Plans
Based on your genetic data, dermatologists can recommend specific treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, or natural remedies more effectively. - Avoid Trial-and-Error
Skip ineffective shampoos and supplements by targeting your specific genetic cause of hair loss. - Supports Medical Guidance
Your dermatologist can use the test results to create a customized and science-backed action plan. - Long-Term Planning
Knowing your risk lets you start a long-term care regimen—diet, stress management, scalp health—before significant hair loss begins.
Limitations of Genetic Hair Loss Tests
Despite their benefits, genetic hair loss tests have several limitations:
- They Are Predictive, Not Diagnostic
You might still experience hair loss even if you’re at low genetic risk—or avoid it despite high-risk results. - Environmental and Lifestyle Factors Are Not Included
Stress, hormones, nutrition, medication, and medical conditions (like thyroid issues) play a major role in hair health but are not captured in the test. - Privacy Concerns
Some direct-to-consumer companies may store, share, or sell your genetic data. Always read the privacy policy. - May Cause Unnecessary Worry
For people already anxious about hair loss, a genetic test may heighten anxiety even if symptoms are minimal.
Who Should Consider This Test?
A genetic hair loss test is most useful for:
- People with a strong family history of hair loss.
- Those who notice early thinning or want to act preventively.
- Individuals interested in personalized treatment plans.
- Patients uncertain about trying finasteride, minoxidil, or DHT blockers.
- Anyone seeking more clarity before investing in long-term treatments like PRP or hair transplants.
Alternatives and Complementary Assessments
Besides genetic tests, several other tools help assess or monitor hair loss:
- Scalp Microscopy: Identifies miniaturized follicles.
- Hair Pull Test: Determines active shedding levels.
- Blood Tests: Check for iron, vitamin D, thyroid levels, etc.
- Dermoscopic Imaging: Tracks changes in hair thickness and follicle activity.
Combining genetic testing with these diagnostic tools offers a more complete picture of your hair health.
Best Practices After Receiving Your Results
After you receive your genetic test results:
- Consult a Dermatologist
Don’t rely solely on at-home test reports. A certified hair specialist can interpret your genetic risk alongside your clinical symptoms. - Start a Prevention Plan
Treatments may include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride (for men), anti-inflammatory shampoos, PRP, or nutritional supplements. - Track Your Progress
Use photos, trichoscopy, or scalp scans to evaluate improvement every 3–6 months. - Adjust Lifestyle
Incorporate stress management, proper scalp hygiene, and a nutrient-rich diet to complement your genetic plan.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
In some countries, your genetic test results may be protected under laws such as GINA (Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act) in the U.S. However, direct-to-consumer companies often operate under less strict rules than medical labs.
Important points:
- Always check if your data is shared with third parties.
- Consider whether storing your genetic data is secure.
- Avoid sending tests to companies with unclear policies.
FAQs
1. Are genetic hair loss tests accurate?
They offer ~70–80% accuracy in predicting pattern baldness based on multiple gene analysis.
2. Does a low-risk result mean I won’t lose hair?
No—many factors like hormones, stress, diet, and medical conditions also affect hair health.
3. Can this test predict alopecia areata?
Tests are mainly designed for androgenetic alopecia; autoimmune types like alopecia areata involve different genes and aren’t typically covered.
4. What’s the cost range?
Expect $100–$300 for most consumer tests; higher prices exist for full genome analysis.
5. Will results impact my insurance or employment?
In many countries, genetic information is protected (e.g., GINA in the U.S.), but read the provider’s privacy policy before testing.
Ready to Take Your Next Step
Genetic hair loss tests provide a valuable early-warning system for people at risk of hereditary baldness. While they can’t offer guarantees, they equip you with knowledge, enabling personalized, proactive treatment strategies.
Used wisely and Consult with Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon in Islamabad today, they help reduce hair loss anxiety and allow you to take timely action—long before hair thinning becomes visible.