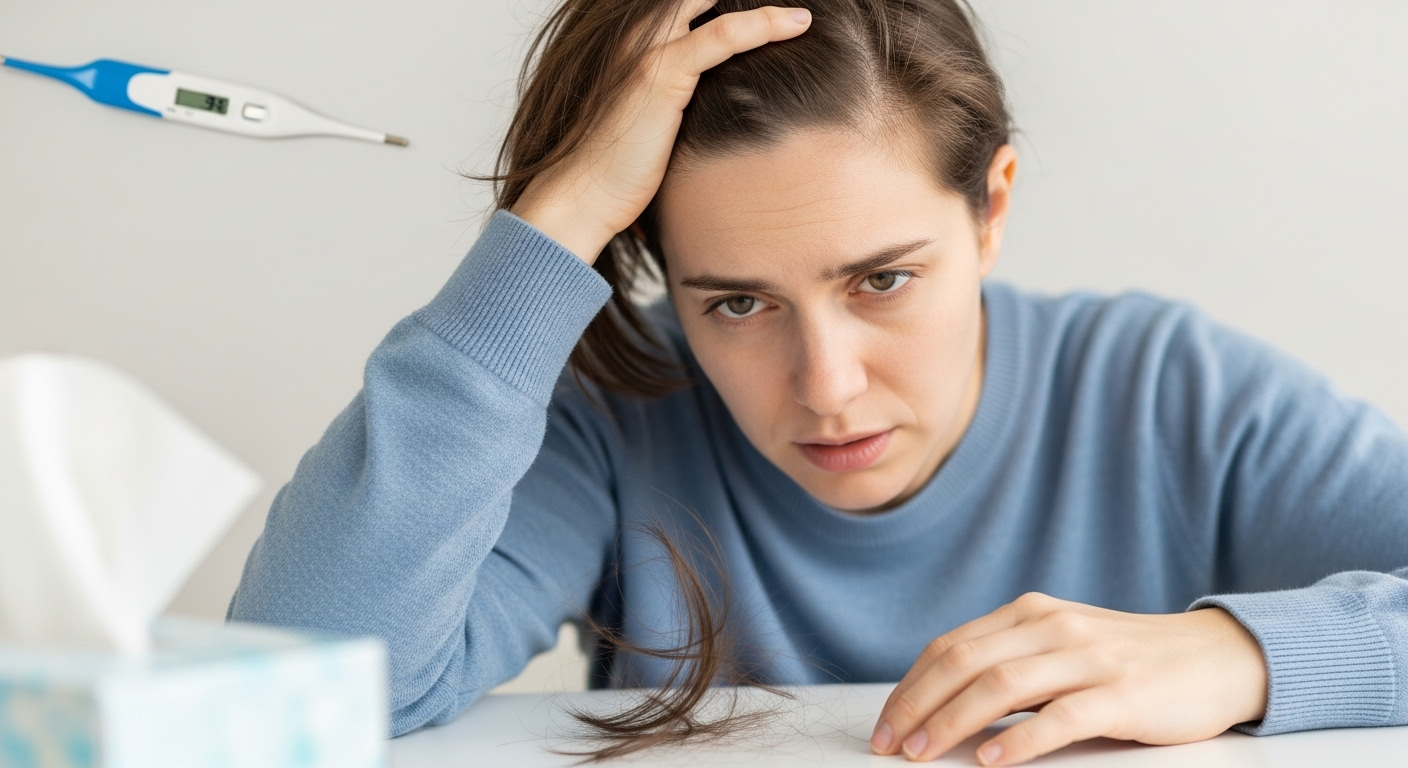
Noticing unexpected shedding weeks after the flu can be stressful—and many people ask, can the flu cause hair loss? The answer is yes: a temporary condition called telogen effluvium is often triggered by illness and fever. In this guide, you’ll learn why flu related hair loss happens, how long recovery takes, and expert-backed tips to …
Noticing unexpected shedding weeks after the flu can be stressful—and many people ask, can the flu cause hair loss? The answer is yes: a temporary condition called telogen effluvium is often triggered by illness and fever.
In this guide, you’ll learn why flu related hair loss happens, how long recovery takes, and expert-backed tips to restore growth. With clear timelines, medical insight, and practical recovery steps, you’ll gain the knowledge and reassurance to manage this condition with confidence.

Why the Flu Can Trigger Hair Loss
Understanding Telogen Effluvium
Hair does not grow continuously—it follows a cycle:
- Anagen (growth phase): lasts 2–7 years.
- Catagen (transition phase): about 2 weeks.
- Telogen (resting phase): about 3 months.
In telogen effluvium, a larger-than-usual number of hairs enter the resting phase, causing noticeable shedding later.
How Flu and Fever Disrupt the Hair Growth Cycle
When your body fights a strong infection like the flu, it prioritizes vital functions such as healing over non-essential processes like hair growth. High fevers, inflammation, and reduced immunity disrupt the normal rhythm of the hair cycle. This “shock” effect explains why shedding may begin several weeks after recovery.
The Role of Stress and Weakened Immunity
Apart from physical illness, mental stress, poor sleep, and nutritional gaps during flu recovery worsen hair shedding. Dermatologists confirm that both biological and psychological stressors can push follicles into premature resting.
Timeline of Can the Flu Cause Hair Loss
Onset of Shedding (6–12 Weeks After Illness)
Most people notice shedding 6–12 weeks after the flu, long after initial symptoms resolve. This delay often makes it hard to connect the dots between illness and hair loss.
Duration and Recovery (3–12 Months)
- Mild cases: noticeable regrowth within 3–6 months.
- Severe cases: may take up to 12 months.
- Encouraging note: flu-related hair loss is almost always temporary and reversible.
Recognizing Symptoms — Is It Just Hair Shedding?
Signs of Telogen Effluvium
- Diffuse thinning across the scalp, not isolated patches
- Increased shedding while brushing or washing
- Reduction in overall hair density but no scarring or inflammation
When It Might Be Something Else
- Alopecia areata: sudden round bald patches
- Pattern baldness: gradual thinning at hairline or crown
- Scalp conditions: redness, scaling, itching
Recovery Tips :How to Support Hair Regrowth
Nutrition & Supplements
- Protein: eggs, fish, and legumes strengthen keratin.
- Iron: prevents anemia-linked shedding.
- Biotin and Zinc: boost follicle health.
- Hydration: supports body repair during recovery.
Stress Management & Lifestyle Balance
- Practice deep breathing, yoga, or meditation.
- Maintain 7–8 hours of quality sleep.
- Avoid tight hairstyles, harsh chemicals, or excessive heat styling.
Medical Treatments
- Topical minoxidil: may speed up regrowth.
- Low-level laser therapy: improves scalp circulation.
- Blood tests: rule out thyroid disease, anemia, or vitamin deficiencies.
When to Seek Medical Help
Red Flags
- Shedding persists longer than 12 months
- Sudden clumps or bald patches appear
- Associated fatigue, weight changes, or dizziness
What Doctors Typically Do
- Scalp exam (pull test, trichoscopy)
- Blood tests for iron, thyroid, and vitamin levels
- Treatment plan customized to underlying health
FAQs
1. How long after the flu does hair loss begin?
Typically 6–12 weeks post-recovery.
2. Will my hair grow back fully?
Yes. Most cases resolve naturally in 3–12 months.
3. Can getting the flu vaccine prevent hair loss?
Yes—indirectly. Vaccination lowers the risk of severe illness, reducing telogen effluvium triggers.
4. Is flu-related hair loss permanent?
No. Unlike genetic baldness, flu hair loss is temporary.
5. What’s the difference between flu hair loss and alopecia areata?
Flu hair loss = diffuse thinning. Alopecia areata = patchy bald spots.
Ready To Take Your Next Step
If you’re experiencing shedding after the flu, don’t panic. With expert care, hair recovery is possible and expected.
Book a consultation with Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon in Islamabad today for a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan. Take the first step toward regaining fuller, healthier hair.