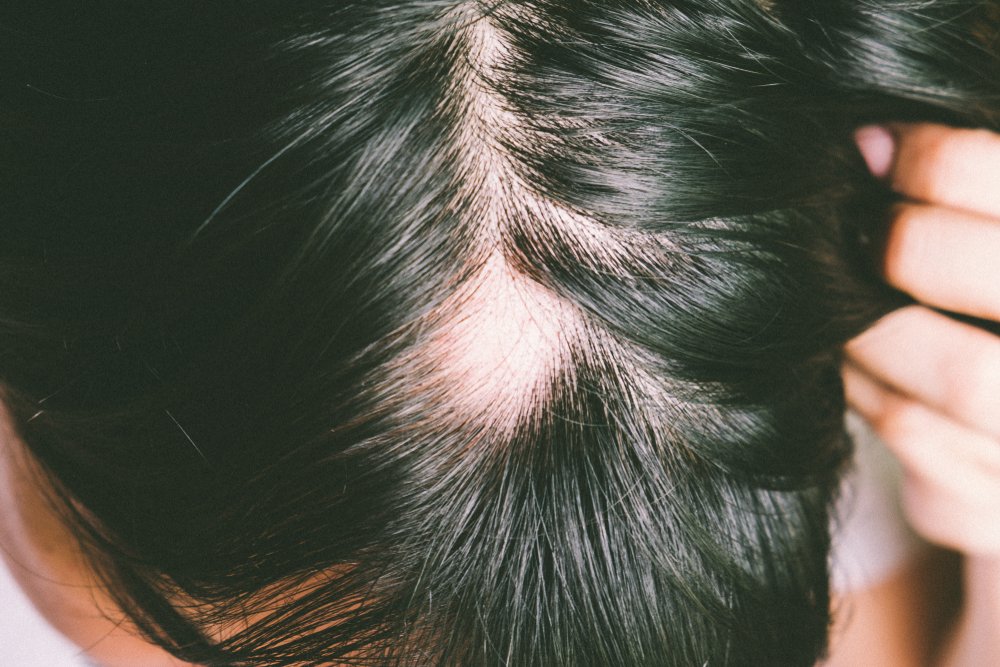
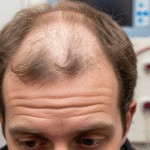
What Is Scarring Alopecia? Scarring Alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, refers to a group of rare conditions that result in permanent hair loss. Unlike other forms of hair loss, where hair follicles remain intact, scarring alopecia leads to the destruction of these follicles, replacing them with scar tissue. This type of hair loss is …
What Is Scarring Alopecia? Scarring Alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, refers to a group of rare conditions that result in permanent hair loss. Unlike other forms of hair loss, where hair follicles remain intact, scarring alopecia leads to the destruction of these follicles, replacing them with scar tissue.
This type of hair loss is irreversible, making early detection and intervention essential for preventing further damage.
The Mechanism Behind Scarring Alopecia
The inflammation caused by scarring alopecia targets the upper part of the hair follicle. This results in the destruction of both the follicle and the sebaceous glands. Over time, the damaged follicles are replaced with scar tissue, leading to permanent hair loss.
Common Types of Scarring Alopecia
There are several types of scarring alopecia, each with its own characteristics and impact on the scalp. Understanding the type you’re dealing with is essential for proper treatment.
1. Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA)
- Characteristics: Most commonly found in Black women, CCCA begins at the crown and gradually spreads outwards. The condition is often associated with inflammation and follicular destruction.
- Causes: Genetic factors, scalp trauma, and inflammatory conditions contribute to CCCA.
2. Lichen Planopilaris (LPP)
- Characteristics: LPP usually affects middle-aged women and presents with inflammation, itching, and eventual hair loss on the scalp.
- Causes: It is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles.
3. Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)
- Characteristics: FFA typically causes a receding hairline and loss of eyebrows, mostly in postmenopausal women.
- Causes: Hormonal changes and autoimmune factors are believed to contribute to this condition.
4. Folliculitis Decalvans
- Characteristics: Folliculitis decalvans leads to chronic inflammation of the hair follicles, resulting in scarring and permanent hair loss.
- Causes: Bacterial infections and immune system dysfunctions are often involved.
Symptoms to Watch For
Detecting scarring alopecia early can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Here are some symptoms to look out for:
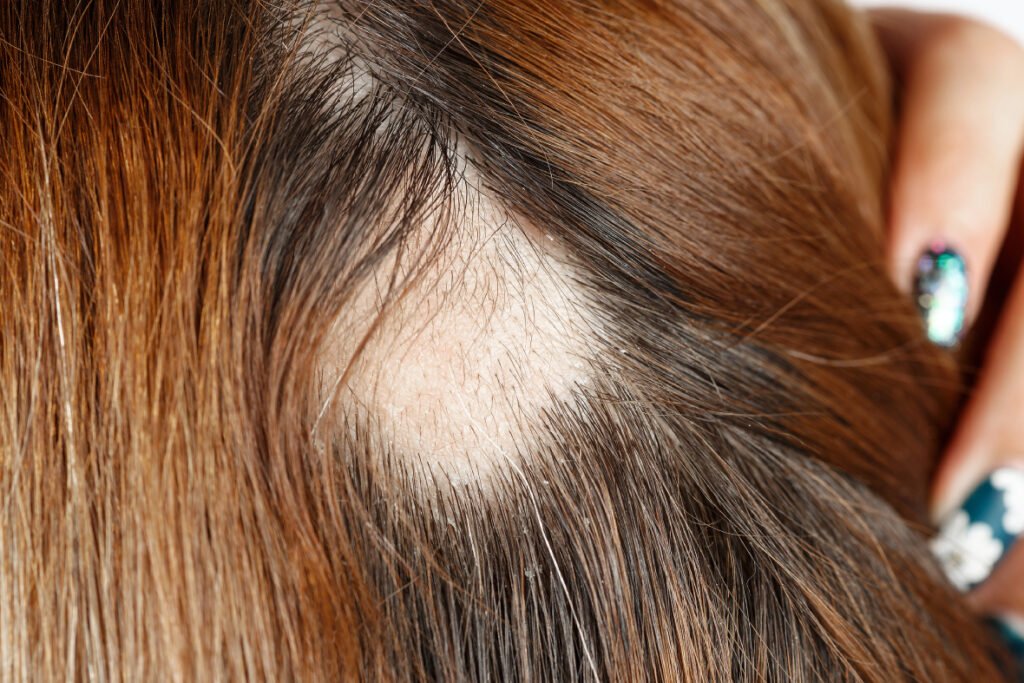
1. Hair Loss Patterns
Unlike regular hair thinning, scarring alopecia often causes hair loss in patches. The pattern may be irregular, and the scalp may show smooth, shiny patches of skin where hair once grew.
2. Scalp Changes
Redness, scaling, pustules, or blisters on the scalp are common symptoms. In some cases, the skin may appear inflamed or irritated.
3. Sensory Symptoms
Itching, burning, or a sensation of tenderness in the affected area can be an early sign of scarring alopecia.
4. Advanced Signs
As the condition progresses, the affected areas may develop smooth, shiny skin, a telltale sign of scarring, and follicle destruction.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the underlying causes of scarring alopecia is crucial for managing and preventing the condition. Some of the primary causes include:
1. Inflammatory Disorders
Scarring alopecia is often linked to autoimmune conditions where the body’s immune system attacks healthy hair follicles.
2. Genetic Predisposition
If you have a family history of scarring alopecia, you may be at a higher risk of developing it yourself.
3. Environmental Triggers
Scalp trauma, infections, burns, or other external factors may trigger or worsen scarring alopecia in some individuals.
4. Hormonal Influences
Hormonal changes, particularly in postmenopausal women, can contribute to conditions like Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA).
Diagnosis: How Is Scarring Alopecia Identified?
Proper diagnosis is key to managing scarring alopecia effectively. A dermatologist typically uses several methods to confirm the condition:
1. Clinical Examination
A thorough examination of the scalp can help identify hair loss patterns and signs of inflammation. The doctor may also evaluate the overall health of the scalp.
2. Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy involves removing a small sample of skin from the affected area to examine the presence of inflammation and scarring under a microscope.
3. Blood Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to rule out underlying systemic conditions that could be contributing to the hair loss.
4. Dermoscopy
A dermoscope is a magnifying device that allows the dermatologist to inspect the scalp and hair follicles for signs of scarring or inflammation.
Treatment Options for Scarring Alopecia
While there is no cure for scarring alopecia, there are several treatments that can help manage the condition and prevent further hair loss.
1. Medications
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Corticosteroids, hydroxychloroquine, and other medications help reduce inflammation and may prevent further follicular damage.
- Antibiotics: If folliculitis decalvans is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to address bacterial infections.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases of autoimmune-related scarring alopecia, immunosuppressant drugs may be used to control the immune system’s attack on hair follicles.
2. Hair Restoration Treatments
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP therapy is an emerging treatment that uses the patient’s own blood to stimulate hair growth in certain types of alopecia.
- Hair Transplants: While hair transplants are typically not recommended for scarring alopecia due to the damage to the hair follicles, they may be an option for patients whose condition has stabilized.
3. Supportive Therapies
- Low-Level Laser Therapy: This treatment uses light energy to stimulate hair growth and improve scalp health.
- Nutritional Supplements: Supplements like biotin, zinc, and iron may help improve hair health and prevent further damage.
Living with Scarring Alopecia: Coping Strategies
Dealing with permanent hair loss can be emotionally challenging. Here are some ways to cope:
1. Psychological Impact
The emotional toll of scarring alopecia can be significant. Talking to a mental health professional or support group can be beneficial.
2. Support Groups
Connecting with others who are experiencing scarring alopecia can provide emotional support and practical advice.
3. Cosmetic Solutions
Wigs, scarves, and hairpieces can help manage the appearance of hair loss and boost confidence.
4. Ongoing Care
Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are crucial to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
FAQs
Can hair grow back after scarring alopecia?
Once the hair follicles are destroyed, hair regrowth is unlikely. However, early intervention can prevent further hair loss and slow the progression.
Is scarring alopecia contagious?
No, scarring alopecia is not contagious. It is a result of an autoimmune response or inflammation.
How can I prevent scarring alopecia?
While some cases are genetic or autoimmune-related, avoiding scalp trauma, treating scalp infections promptly, and seeking early treatment can help prevent or manage scarring alopecia.
Book a Consultation Today
If you’re experiencing symptoms of scarring alopecia, don’t wait. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference. Book a consultation with Dr. Uzma Irfan, an ISHRS-certified surgeon in Islamabad today to ensure effective management of your condition and prevent further hair loss.